
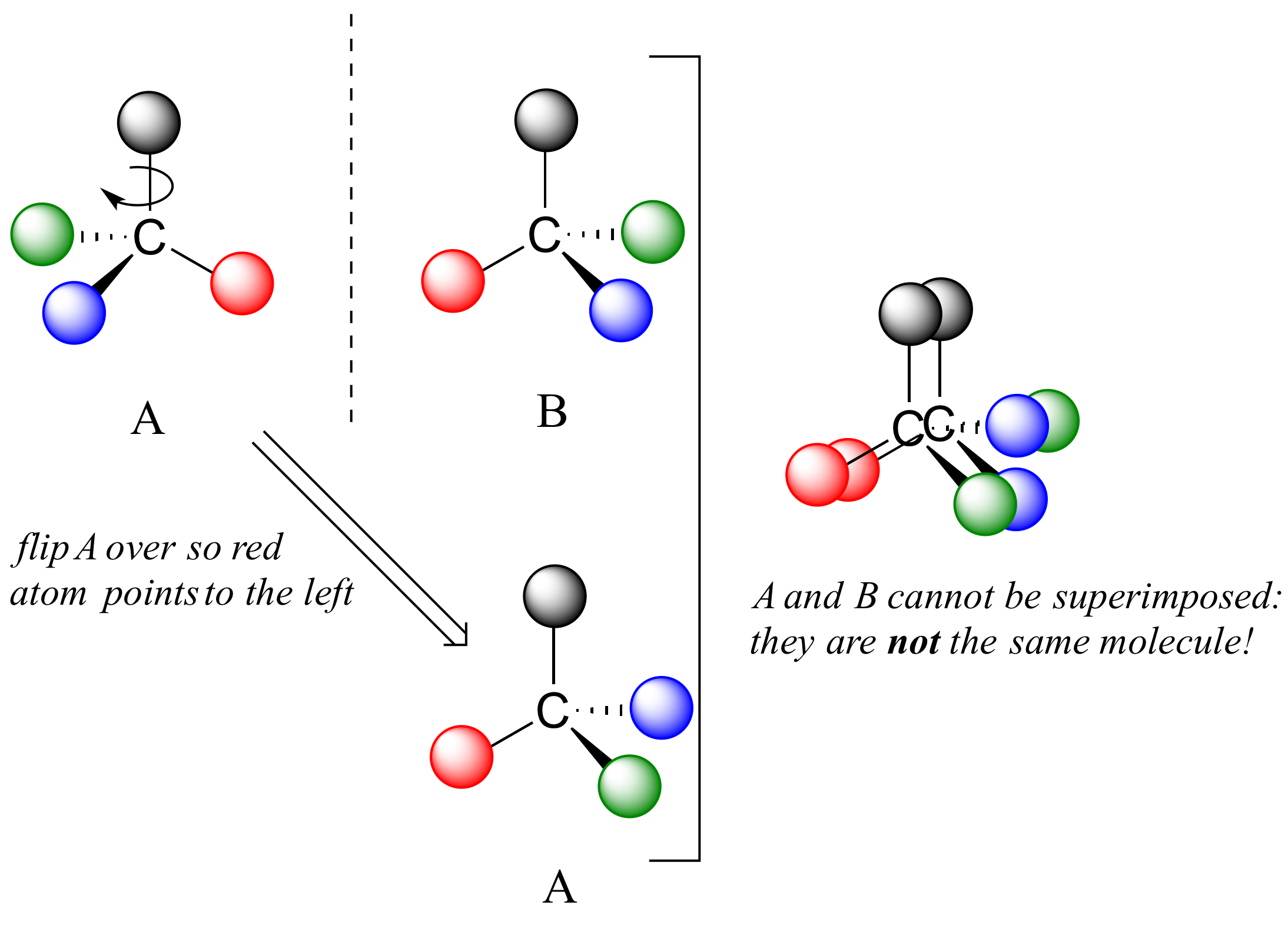
(b) In contrast, dichlorofluoromethane and its mirror image can be rotated so they are superimposable. To superimpose the mirror images, bonds must be broken and reformed. Rotation of its mirror image does not generate the original structure. In the pyranose form of glucose, carbon-1 is chiral. (a) Bromochlorofluoromethane is a chiral molecule whose stereocenter is designated with an asterisk. When there is more than one chiral center in a carbohydrate, look at the chiral carbon farthest from.

The rest is one of two cyclic forms of glucose formed when the hydroxyl group on carbon 5 (C 5) bonds to the aldehyde carbon 1 (C 1), as shown below.\): Comparison of Chiral and Achiral Molecules. The linear form of glucose shown above makes up less than 3% of the glucose molecules in a water solution. The functional groups are the aldehyde and hydroxyl groups.īecause of these polar functional groups, glucose (and other monosaccharides) are highly soluble in water (1.5 g/mL at 25 ✬). The carbon atom that forms the new chiral center (C-1) is called the anomeric carbon. Owens Corning FOAMULAR & FOAMULAR NGX 250 Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Rigid Foam Insulation is a closed cell, highly. When a molecule such as glucose converts to a cyclic form, it generates a new chiral center at C-1. I know that more than 99.5 of glucose exists as Haworth Projection - Closed Ring Structure and hence Linear - Fischer Projection practically does. Glucose and mannose are epimers that differ at the C-2 carbon, while glucose and galactose are epimers that differ at the C-4 carbon, as shown below. This happens through the nucleophilic attack of the hydroxyl group at the. Note: Chiral carbon atoms are the carbon atoms which lack symmetry and have four different substituents attached to it. \beta -D(+)-glucose has 5 chiral carbons. They are formed when an alcohol oxygen atom adds to the carbonyl carbon of an aldehyde or a ketone. -D-glucose does not have a plane of symmetry and thus, the carbon atoms are different. Most chiral organic molecules have at least one carbon atom that is bonded to four different. (b) The unmarked flask is achiral because it can be superimposed on its mirror image. Click on the mouse at left to clear the text and reset the image. Fischer Projection: 4 chiral centres Haworth Projection: 5 chiral centres My doubt is that is there any (specific) method (practical) to ascertain the number of chiral centres in both the forms. Before we get into the discussion of cyclic hemiacetals and hemiacetals, let’s just quickly recollect how they are formed. (a) Objects that are nonsuperimposable mirror images of each other are chiral, such as the left and the right hand. One structure of glucose is shown below.Ĭlick on the step numbers below to see some important things about glucose's structure. The schematic structure of cellulose (e.g. All are known - some occur naturally and the others have been synthesized (see Table 20-1). d-Glucose is an aldohexose type sugar, occurring generally in six-membered ring form (- and -glucopyranose, see Carbohydrates Figure 3).Together with its 1-4-gucoside polymer, cellulose, d-glucose is the most abundant organic matter in the terrestrial biosp here (Kamide, 2005). Glucose is called a monosaccharideīecause it forms one simple building block of more complicated carbohydrates. The carbons labeled with an asterisk in 1 are chiral thus there are 2 4, or sixteen, possible configurational isomers. By reacting the OH group on the fifth carbon atom with the aldehyde group, the. We prepared a few D-carbon dots using D-methionine, D-glucose. For instance, galactose and glucose are both aldohexoses, but have different physical structures and chemical properties. This gives rise to a number of isomeric forms, all with the same chemical formula. D-Glucose can be represented with a Fischer projection (a) or three dimensionally (b). In this work, we have successfully prepared chiral carbon dots from chiral precursors. Each carbon atom that supports a hydroxyl group is chiral, except those at the end of the chain.

9 Glucose and fructose give positive Tollen's test as they reducing sugar because of the. There are four chiral carbon atoms in the open-chain form of glucose. One of the most important carbohydrates in the body is glucose (C 6H 12O 6). The same is true for monosaccharides that form cyclic structures: rings consisting of five or six carbon atoms are the most stable. carbon is towards right and hence, all have D-configuration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
